Answer Unlock Previous question Next question Transcribed image text: At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is = (2.00m) i + (4.00 m) Î – (3.00m) ſ, its velocity is =- (6.76 m/s) î + (2.41 m/s) Î + (6.07 m/s) k and it is subject to a force 7 = 16.95 N) î – (1.44N) Î + (5.32 N) Î.
Preview Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics Workbook by Cambridge International Education – Issuu
At one instant force F = 4. 0 J ^ N acts on a 0. 2 5 k g object that has position vector r = (2. 0 i ^ − 2. 0 k ^) m and velocity vector v = (− 5. 0 i ^ + 5. 0 k ^) m / s. About the origin and in unit vector notation, what are the torque acting on the object?
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Physics questions and answers. At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d→ = (2.00 m) î + (4.00 m) ĵ – (3.00 m) k̂, its velocity is v→ = – (5.43m/s) î + (2.11 m/s) ĵ + (3.73 m/s) k̂ and it is subject to a force F→ = (3.80 N) î – (7.65 N) ĵ + (7.63 N) k̂. Find the acceleration of the

Source Image: yumpu.com
Download Image
H C VERMA PHYSICS BOOK SOLUTIONS WORK POWER ENERGY
Q → View Solution Q Click here:point_up_2:to get an answer to your question :writing_hand:at the instant the displacement of a 200 kg object relative to the origin is 4

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
At The Instant The Displacement Of A 2.00kg
Q → View Solution Q Click here:point_up_2:to get an answer to your question :writing_hand:at the instant the displacement of a 200 kg object relative to the origin is 4
problem. 11.30. We have an object. It’s two kilograms and mass. It’s Ah, moving around at a particular moment in time. It’s in this position going with this velocity and with this force acting upon it and we want to find out a few things, we want to know what its acceleration is, and then its angular momentum and talk about the origin.
SOLVED: A hammerhead of mass m=2.00 kg is allowed to fall onto a nail from a height h=0.400 m . Calculate the maximum amount of work it could do on the nail
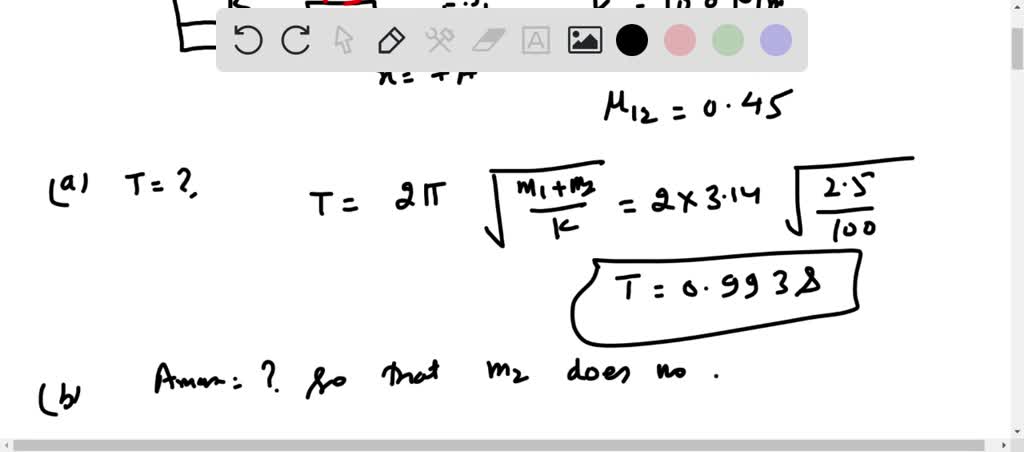
At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is = (2.00 m) + (4.00 m) j = (3.00 m), its velocity is = – (8.80 m/s) + (8.53 m/s) + (9.01 m/s) and it is subject to a force = (4.53 N) i – (2.58 N) j + (8.77 N) Find the acceleration of the object ( (a), (b) and (c) for and k components respectively), the angular
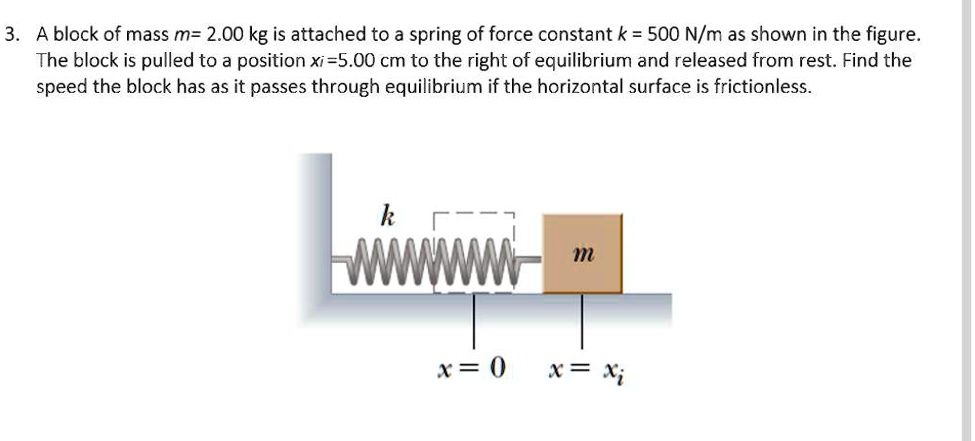
SOLVED: A block of mass m= 2.00 kg is attached to a spring of force constant k = 500 N/m as shown in the figure The block is pulled to a position
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
A sinusoidal sound wave moves through a medium and is descri | Quizlet
At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is = (2.00 m) + (4.00 m) j = (3.00 m), its velocity is = – (8.80 m/s) + (8.53 m/s) + (9.01 m/s) and it is subject to a force = (4.53 N) i – (2.58 N) j + (8.77 N) Find the acceleration of the object ( (a), (b) and (c) for and k components respectively), the angular
Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
Preview Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics Workbook by Cambridge International Education – Issuu
Answer Unlock Previous question Next question Transcribed image text: At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is = (2.00m) i + (4.00 m) Î – (3.00m) ſ, its velocity is =- (6.76 m/s) î + (2.41 m/s) Î + (6.07 m/s) k and it is subject to a force 7 = 16.95 N) î – (1.44N) Î + (5.32 N) Î.

Source Image: issuu.com
Download Image
H C VERMA PHYSICS BOOK SOLUTIONS WORK POWER ENERGY
Physics questions and answers. At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d→ = (2.00 m) î + (4.00 m) ĵ – (3.00 m) k̂, its velocity is v→ = – (5.43m/s) î + (2.11 m/s) ĵ + (3.73 m/s) k̂ and it is subject to a force F→ = (3.80 N) î – (7.65 N) ĵ + (7.63 N) k̂. Find the acceleration of the
Source Image: studymaterialkota.com
Download Image
Sem 1 Practice Final | PDF | Force | Entropy
At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is = (2.00 m) + (4.00 m) – (3.00 m) K, its velocity is = (2.61 m/s) + (1.57 m/s) + (6.37 m/s) R and it is subject to a force = (1.47 N) – (8.39 N) I + (8.16 N) Find the acceleration of the object ((a), (b) and (c) for , i and k components respectively) (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
A sled with a rider having a combined mass of 125 kg travels | Quizlet
Q → View Solution Q Click here:point_up_2:to get an answer to your question :writing_hand:at the instant the displacement of a 200 kg object relative to the origin is 4

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
6.1 Solving Problems with Newton’s Laws | University Physics Volume 1
problem. 11.30. We have an object. It’s two kilograms and mass. It’s Ah, moving around at a particular moment in time. It’s in this position going with this velocity and with this force acting upon it and we want to find out a few things, we want to know what its acceleration is, and then its angular momentum and talk about the origin.

Source Image: courses.lumenlearning.com
Download Image
A sinusoidal sound wave moves through a medium and is descri | Quizlet
6.1 Solving Problems with Newton’s Laws | University Physics Volume 1
At one instant force F = 4. 0 J ^ N acts on a 0. 2 5 k g object that has position vector r = (2. 0 i ^ − 2. 0 k ^) m and velocity vector v = (− 5. 0 i ^ + 5. 0 k ^) m / s. About the origin and in unit vector notation, what are the torque acting on the object?
H C VERMA PHYSICS BOOK SOLUTIONS WORK POWER ENERGY A sled with a rider having a combined mass of 125 kg travels | Quizlet
At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is = (2.00 m) + (4.00 m) – (3.00 m) K, its velocity is = (2.61 m/s) + (1.57 m/s) + (6.37 m/s) R and it is subject to a force = (1.47 N) – (8.39 N) I + (8.16 N) Find the acceleration of the object ((a), (b) and (c) for , i and k components respectively) (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units