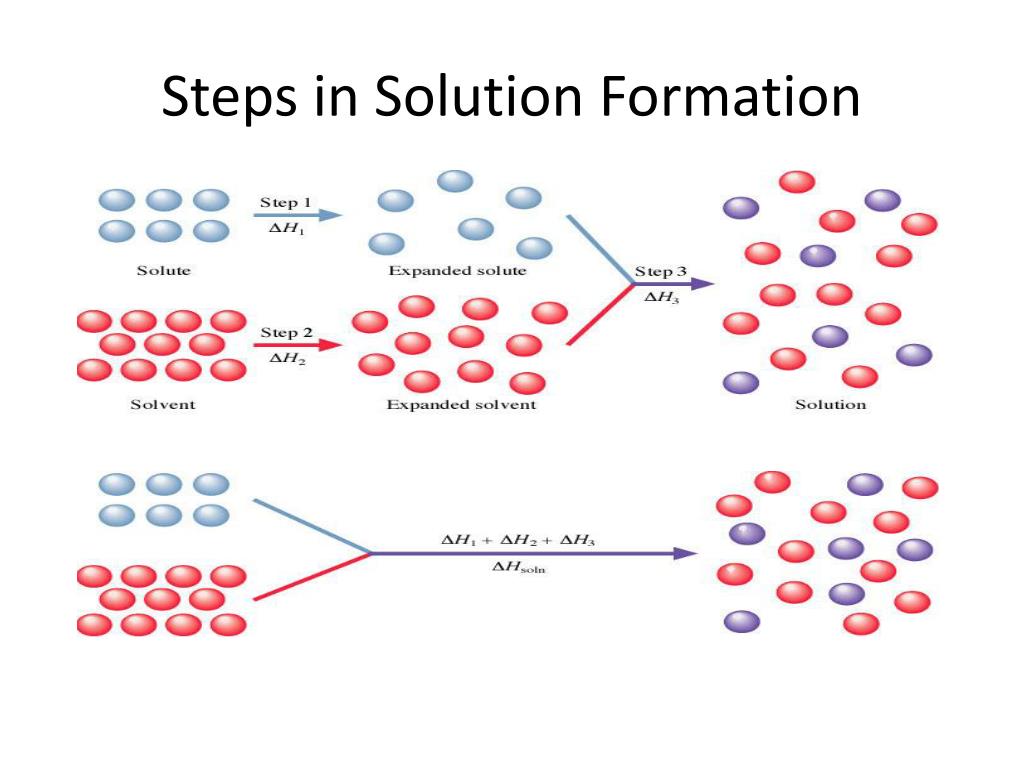
The process occurs in three discrete steps, indicated by ΔH1 Δ H 1, ΔH2 Δ H 2, and ΔH3 Δ H 3 in Figure 13.1.2 13.1. 2. The overall enthalpy change in the formation of the solution ( ΔHsoln Δ H s o l n) is the sum of the enthalpy changes in the three steps: ΔHsoln = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3 (13.1.3) (13.1.3) Δ H s o l n = Δ H 1 + Δ H 2
What type of reaction takes place in the Haber process, exothermic or endothermic? – Quora
The process occurs in three discrete steps, indicated by Δ H1, Δ H2, and Δ H3 in Figure 13.1 “Enthalpy Changes That Accompany the Formation of a Solution“. The overall enthalpy change in the formation of the solution (Δ Hsoln) is the sum of the enthalpy changes in the three steps: Equation 13.3. ΔHsoln = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3.
Source Image: chem.libretexts.org
Download Image
Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Which of the following steps in a solution formation is *exothermic*? a) Overcoming the solute-solute intermolecular forces. b) Overcoming the solvent-solute intermolecular forces. c) Overcoming the solvent-solvent intermolecular forces. d) Establishing the solute-solvent intermolecular forces..
Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
Chapter 6: Solutions. – ppt download 2. The overall enthalpy change in the formation of the solution ( ΔHsoln Δ H s o l n) is the sum of the enthalpy changes in the three steps: ΔHsoln = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3 (13.3.3) (13.3.3) Δ H s o l n = Δ H 1 + Δ H 2 + Δ H 3. When a solvent is added to a solution, steps 1 and 2 are both endothermic because energy is required to overcome

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Which Of The Following Steps In Solution Formation Is Exothermic
2. The overall enthalpy change in the formation of the solution ( ΔHsoln Δ H s o l n) is the sum of the enthalpy changes in the three steps: ΔHsoln = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3 (13.3.3) (13.3.3) Δ H s o l n = Δ H 1 + Δ H 2 + Δ H 3. When a solvent is added to a solution, steps 1 and 2 are both endothermic because energy is required to overcome Jul 12, 2023Solvation can be an exothermic or endothermic process depending on the nature of the solute and solvent. In both cases, step 1, separation of the solvent particles, is energetically uphill (ΔH 1 > 0), as is step 2, separation of the solute particles (ΔH 2 > 0).
Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes, Important Questions & Practice Paper | AglaSem Scho… | Science notes, Chemistry education, Chemistry basics
Exothermic Solvation Processes. This is illustrated in the energy cycle of figure 13.2.2. Since enthalpy is a state function the energy going from solvent and solute to solution is independent of the path, and there are two paths, the direct route, represented in green as \(\Delta\)H soln and that of steps 1,2,3. So 12.3 Energetics of Solution Formation – YouTube

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Exothermic vs. Endothermic: Chemistry’s Give and Take – Discovery Express Exothermic Solvation Processes. This is illustrated in the energy cycle of figure 13.2.2. Since enthalpy is a state function the energy going from solvent and solute to solution is independent of the path, and there are two paths, the direct route, represented in green as \(\Delta\)H soln and that of steps 1,2,3. So

Source Image: discoveryexpresskids.com
Download Image
What type of reaction takes place in the Haber process, exothermic or endothermic? – Quora The process occurs in three discrete steps, indicated by ΔH1 Δ H 1, ΔH2 Δ H 2, and ΔH3 Δ H 3 in Figure 13.1.2 13.1. 2. The overall enthalpy change in the formation of the solution ( ΔHsoln Δ H s o l n) is the sum of the enthalpy changes in the three steps: ΔHsoln = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3 (13.1.3) (13.1.3) Δ H s o l n = Δ H 1 + Δ H 2
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Chapter 6: Solutions. – ppt download Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Which of the following steps in a solution formation is *exothermic*? a) Overcoming the solute-solute intermolecular forces. b) Overcoming the solvent-solute intermolecular forces. c) Overcoming the solvent-solvent intermolecular forces. d) Establishing the solute-solvent intermolecular forces..

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
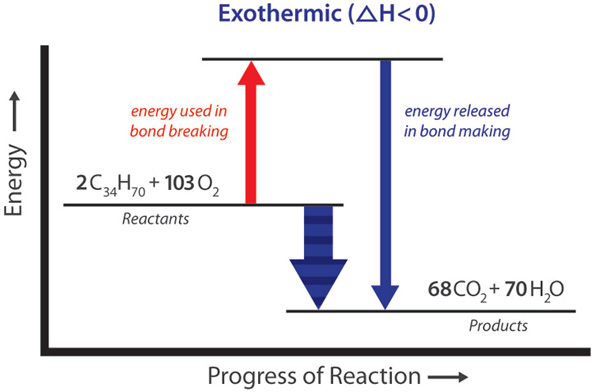
Exothermic, Endothermic, & Chemical Change | Energy Foundations for High School Chemistry From Hess’s law we know that we can add the energies of each step in the cycle to determine the energy of the overall process. Therefore, the energy of solution formation, the enthalpy of solution, equals the sum of the three steps: D H soln = D H 1 + D H 2 + D H 3. The breaking of bonds requires or absorbs energy.
Source Image: highschoolenergy.acs.org
Download Image
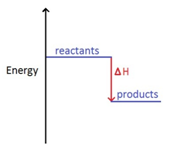
3:05 (Triple only) draw and explain energy level diagrams to represent exothermic and endothermic reactions – TutorMyself Chemistry 2. The overall enthalpy change in the formation of the solution ( ΔHsoln Δ H s o l n) is the sum of the enthalpy changes in the three steps: ΔHsoln = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3 (13.3.3) (13.3.3) Δ H s o l n = Δ H 1 + Δ H 2 + Δ H 3. When a solvent is added to a solution, steps 1 and 2 are both endothermic because energy is required to overcome
Source Image: tutormyself.com
Download Image
AP Chem Turn in Hydrogen Gas Lab Unit 3 Test Th 10/25, Fri 10/26 – ppt download Jul 12, 2023Solvation can be an exothermic or endothermic process depending on the nature of the solute and solvent. In both cases, step 1, separation of the solvent particles, is energetically uphill (ΔH 1 > 0), as is step 2, separation of the solute particles (ΔH 2 > 0).

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Exothermic vs. Endothermic: Chemistry’s Give and Take – Discovery Express
AP Chem Turn in Hydrogen Gas Lab Unit 3 Test Th 10/25, Fri 10/26 – ppt download The process occurs in three discrete steps, indicated by Δ H1, Δ H2, and Δ H3 in Figure 13.1 “Enthalpy Changes That Accompany the Formation of a Solution“. The overall enthalpy change in the formation of the solution (Δ Hsoln) is the sum of the enthalpy changes in the three steps: Equation 13.3. ΔHsoln = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3.
Chapter 6: Solutions. – ppt download 3:05 (Triple only) draw and explain energy level diagrams to represent exothermic and endothermic reactions – TutorMyself Chemistry From Hess’s law we know that we can add the energies of each step in the cycle to determine the energy of the overall process. Therefore, the energy of solution formation, the enthalpy of solution, equals the sum of the three steps: D H soln = D H 1 + D H 2 + D H 3. The breaking of bonds requires or absorbs energy.